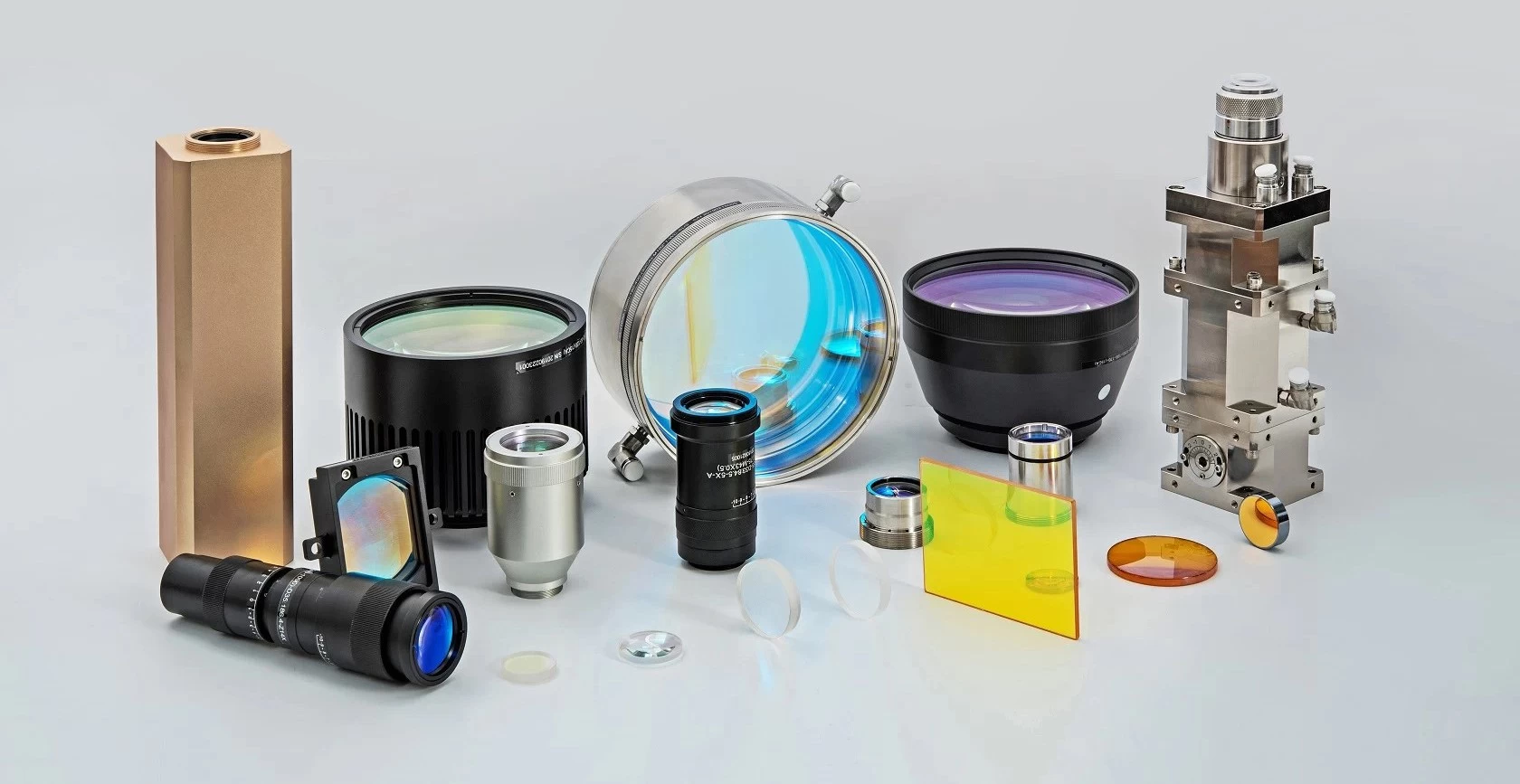
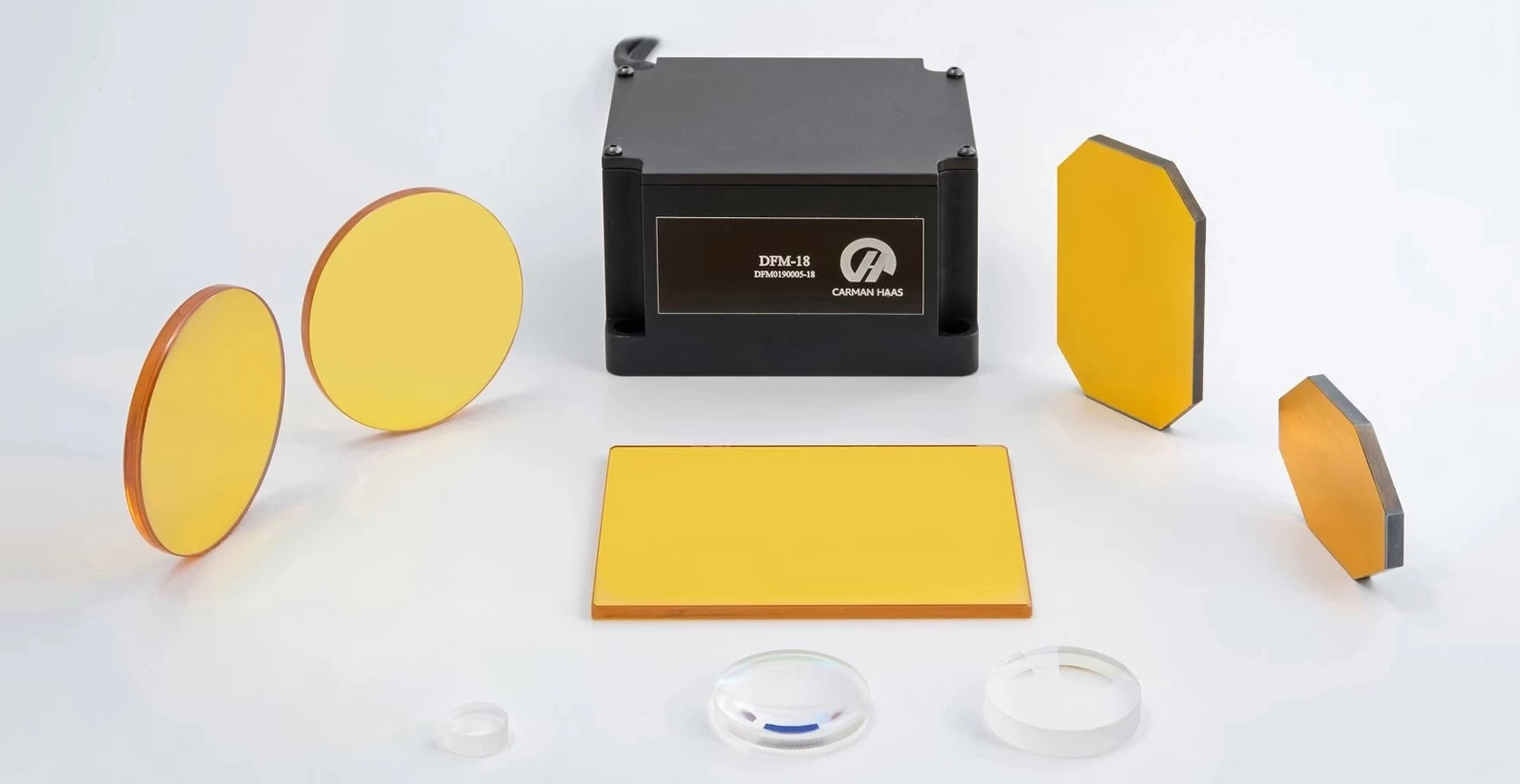
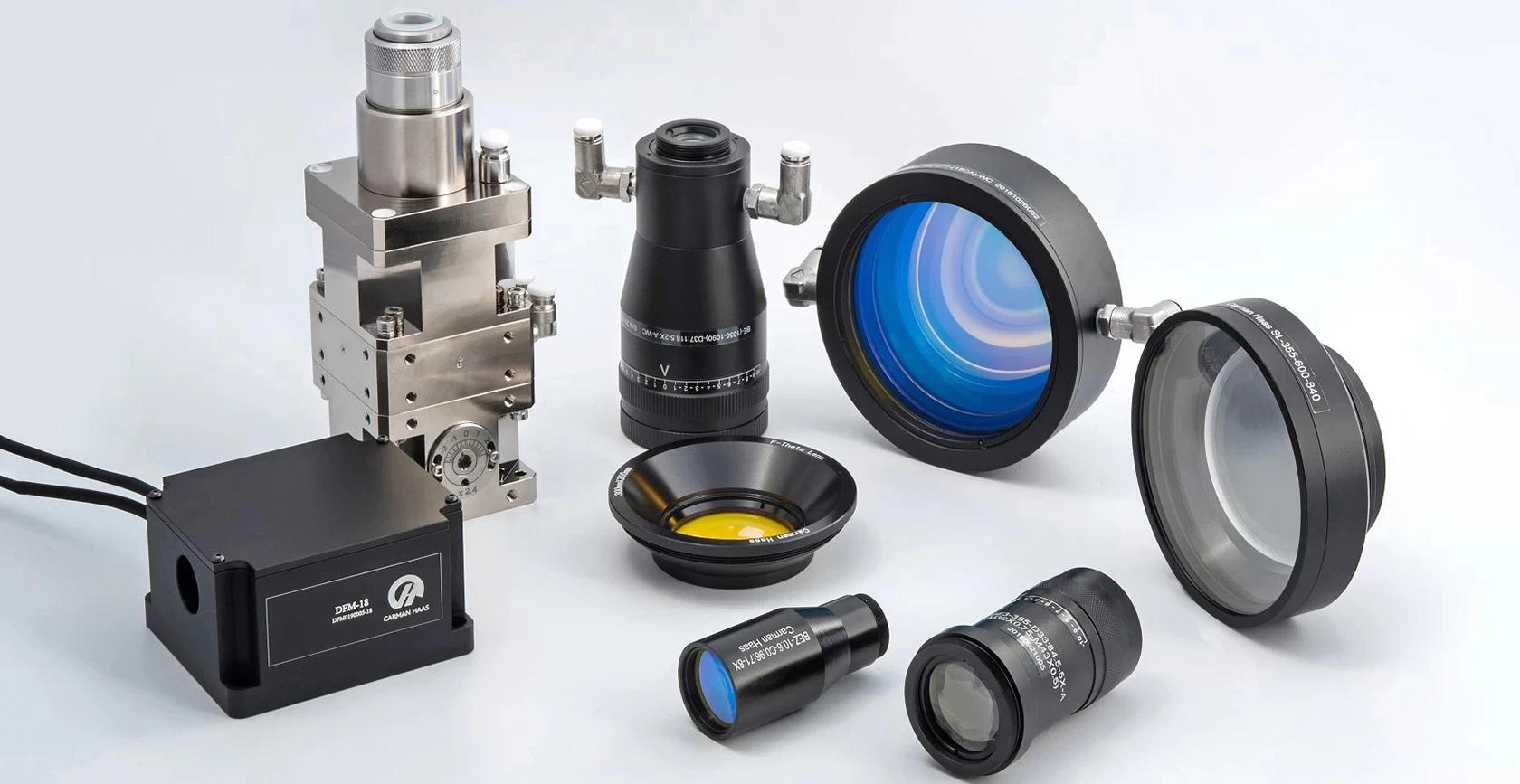
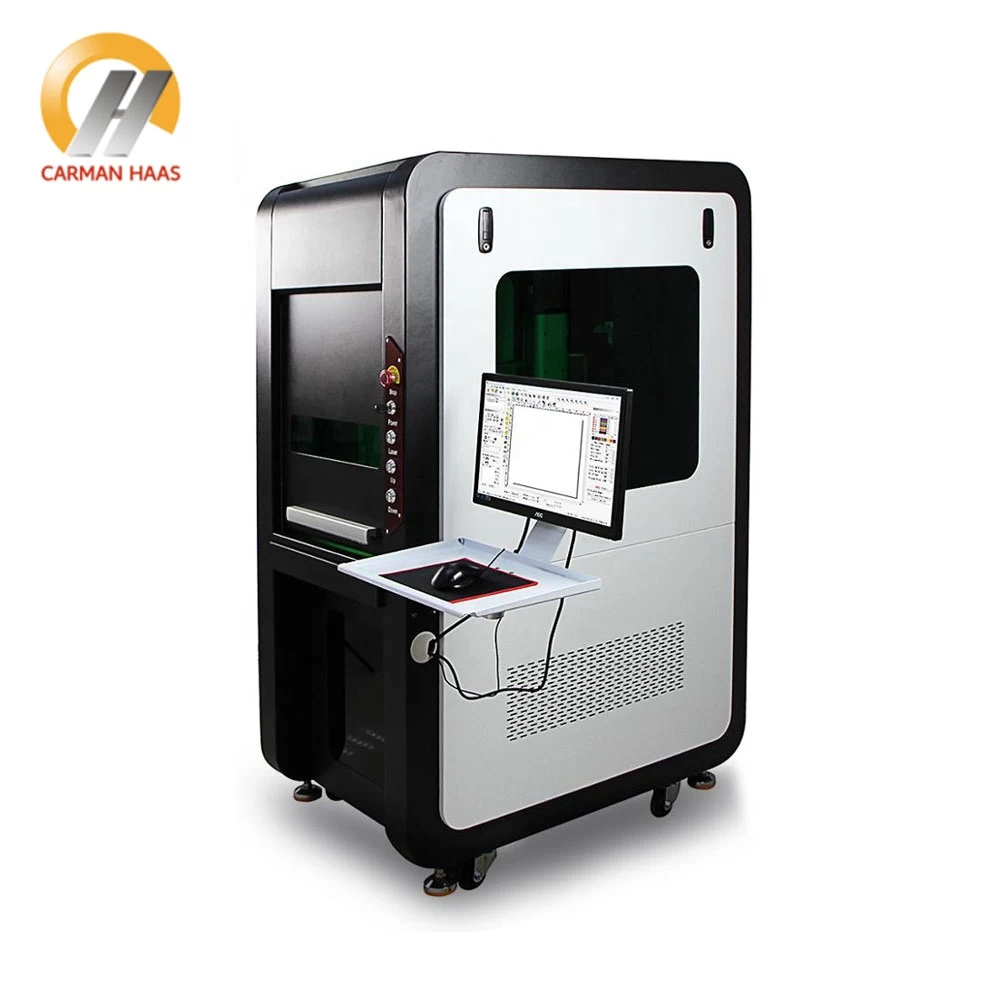
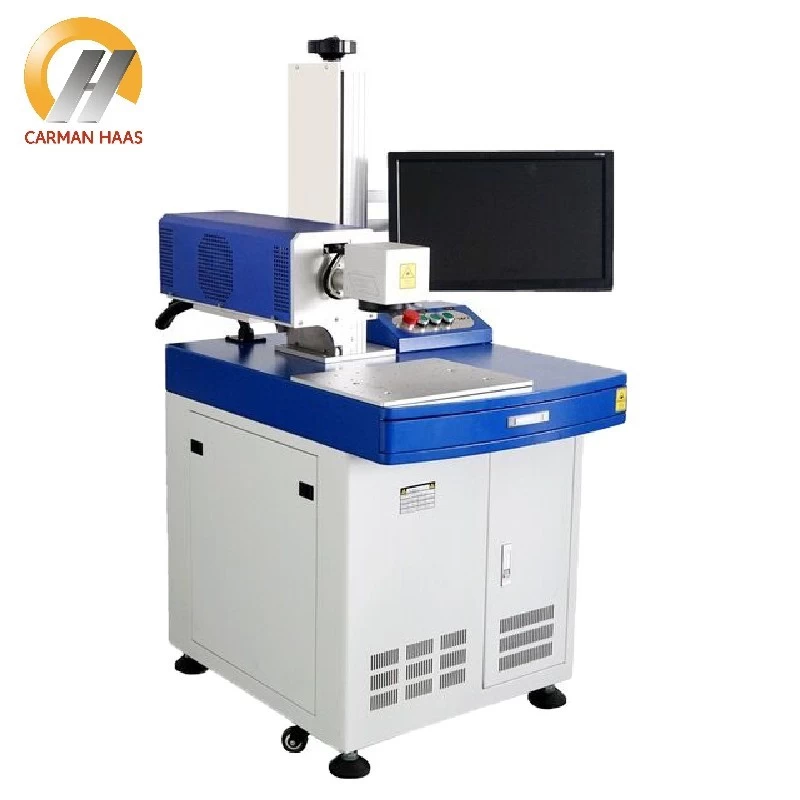
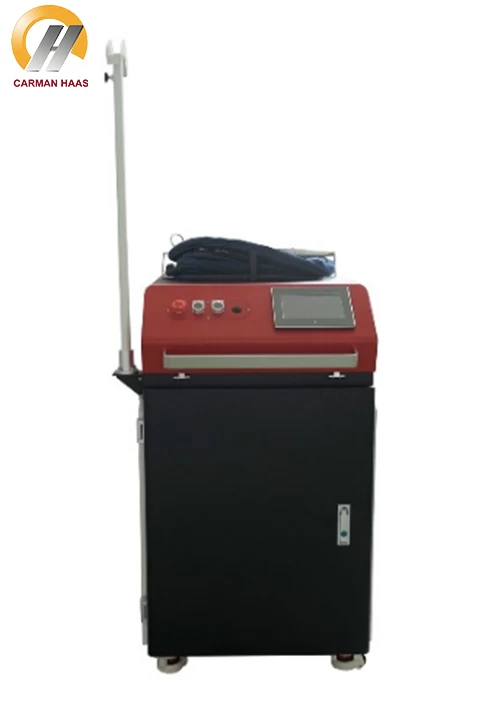
Laser optics production process
If you often use optical components, do you know how they are produced? This article briefly introduces the production process of optical components from four aspects: plane, curved surface, coating and quality inspection.
Plane optics manufacturing
Forming: Cut the whole material into individual optical element blanks. The flat substrate includes calcite, N-BK7, fused silica, SF11 and Schott neutral density glass. The maximum diameter of the circular element is 10 inches, and the maximum side length of the square is 7 inches.

Telecentric f-Theta Lenses Fused Silica
Polishing: After the optical element is formed, the upper plate is polished. The components are glued to the reference pad and polished with a Strasbaugh spindle polishing machine. One surface is polished at a time. The technician will make real-time adjustments based on the interferometer on-line measurement results. Generally, a λ/10 wavefront error and a surface roughness of 3 to 5 Å can be achieved. Slow precision polishing can achieve λ/40 flatness and 1 Å roughness.
Speedfam double-sided polishing is used for some components after forming, and hundreds of components can be polished at a time. The polishing roughness of this equipment is also 3 to 5 Å (double-sided), and the parallelism is as low as 5 arc seconds.
Curved optical manufacturing
Spherical and aspherical surfaces
Satisloh CNC machine tools can produce lenses with diameters from 2 to 150 mm. Technicians can monitor online adjustments through the Zygo interferometer to ensure that the products meet specifications. After the lens reaches the correct curvature, edging and centering are performed. We use the Satisloh centering machine tool to ensure that the axis deviation is as low as 5 arc seconds, which meets the 3 arc minutes specification requirements for most of our optical components.
Diffraction-Limited Aspheric Surface
A QED magnetorheological polishing machine is used to produce diffraction-limited aspheric lenses. This process can achieve surface accuracy within 55 nm, depending on the material being polished.
Aspheric Fused Silica Focusing lens
Metal substrate: Nanotech ultra-precision single point diamond lathe can process metal curved mirrors and special materials mid to far infrared lenses. The lens substrate or mirror is installed on a high-speed rotating shaft, and the single-point diamond turning starts to be polished as it rotates until the desired shape and surface quality are reached.
Optical coating: There are a variety of coating equipment and measurement auxiliary equipment. The coating clean room is maintained at a level of 10,000. The optical components from the manufacturing workshop are first ultrasonically cleaned, and then inspected and cleaned one by one before being loaded into the coating machine.
Final inspection: Quality control is an indispensable part of optical manufacturing. Every optical component must pass quality inspection, which generally includes measuring physical properties, optical performance and environmental strength.
Physical parameter tests include diameter, center thickness, surface flatness, parallelism and surface quality. Optical performance includes wavefront error, focal length and coating performance. Environmental testing can include laser damage threshold, temperature cycling, humidity cycling, and coating strength.

















